Overview
Businesses are increasingly adopting multi-cloud, hybrid-cloud, multi-k8s-cluster deployment strategy for their high availability, disaster recovery, scalability, customer experience and regulatory compliance goals and to maximize the service continuity and uptime. The strategy involves spreading the MongoDb (Postgres/other) database cluster across multiple Kubernetes clusters deployed in multiple data centers, multiple clouds (regions/zones).
KubeSlice can help realize the multi-cluster deployment strategy.
KubeSlice combines network, application, and deployment services in a framework to create tenancy in a Kubernetes cluster and extends it to multi-cluster.
KubeSlice creates logical application boundaries known as slices that allow pods and services to communicate seamlessly across clusters, clouds, edges, and data centers regardless of their physical location. Each slice is assigned its own set of namespaces, resource quotas, traffic profiles that creates an isolated virtual network for each tenant (a team or a customer) in a single cluster or multiple clusters. KubeSlice service discovery enables pods/services to discover and communicate with each other. KubeSlice export/import mechanisms and KubeSlice meshDNS enables service discovery across the slice (across all the clusters registered with slice).
KubeSlice enables Kubernetes clusters to communicate over a slice specific overlay network enabling a seamless communication across the database cluster members (replica sets). The members (replicas) can be distributed across multiple Kubernetes clusters and are reachable over the slice overlay network using the member's FQDN address of the overlay network. By enabling a simplified FQDN/DNS based communication across geographically distributed Kubernetes clusters KubeSlice enables MongoDB (database) cluster members to communicate and coordinate the changes, streaming replication, replication, election, and so on to meet resiliency, consistency and high availability requirements.
KubeSlice creates a slice overlay network across all the clusters with slice VPN gateways and provides service discovery across the slice to provide FQDN/IP based communication between Pods that are deployed on the slice.
KubeSlice does not require Istio or other service mesh to provide FQDN based service discovery across the clusters (across slice).
MongoDB database deployment models can take advantage of KubeSlice connectivity and service discovery (FQDN based) across the slice to spread database members (replica sets) across geographically distributed Kubernetes clusters.
MongoDB (Postgres/other) supports several deployment models based on the business deployment strategy requirements: multi-cloud, hybrid-cloud, multi-k8s-cluster deployment strategy for high-availability, disaster recovery, scalability, customer experience and regulatory compliance goals and to maximize the service continuity and uptime.
The following are some of the multi-cluster deployment models:
- Single cloud/data center for high availability
- Active/Standby deployment for DR in multiple clouds/data centers
- Active/Active sharding based deployment for HA/scalability/in multiple clouds/data centers
- Primary/Secondary replica sets for DR in multiple clouds/data centers
KubeSlice slice can help with the above deployment models with its simplified multi-cluster connectivity
- with secure slice overlay network and service discovery - between replica set members to achieve the MongoDB multi-cluster deployment strategy requirements.
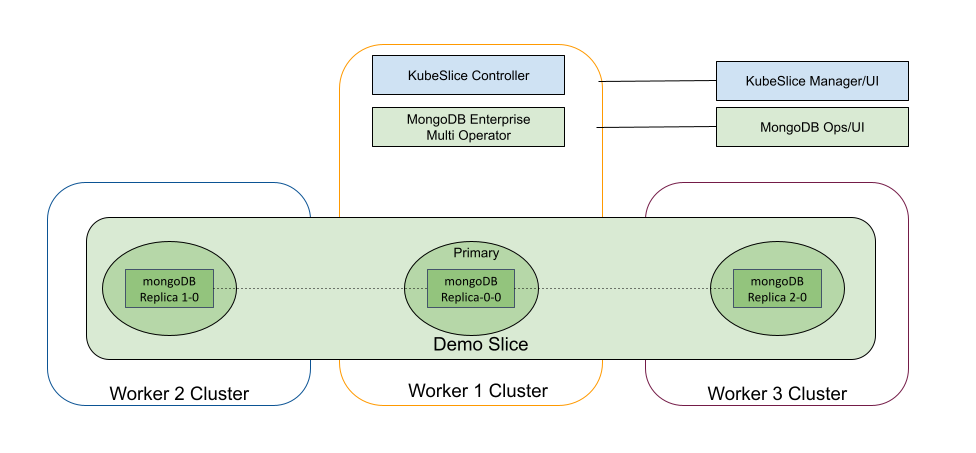
The following figure shows the demo setup with mongoDB replica sets deployed over three clusters.